Process Evaluation of DOE's Weatherization Readiness Fund (WRF)
DOE's Weatherization Assistance Program (WAP) is recognized as a key strategy for reducing energy burdens and carbon emissions in homes occupied by low-income households. Our research provides a preliminary assessment of aspects of the newly established Weatherization Readiness Fund. WRF is designed to mitigate barriers faced by households living in substandard housing that cannot have their homes weatherized by WAP without prior rehabilitation. The Georgia Tech team, in partnership with ORNL, examined several aspects of WRF following its implementation in 2022. 
Task 1 was a case study of WRF implementation and outcomes in Georgia. It revealed that spending by community action agencies (i.e., subgrantees of the Georgia Environmental Facilities Authority) varied significantly during the WRF's first year. On average, WRF in Georgia spent an average of $16,000 per participating household in PY 2023. Most of the funding was spent on roof replacement, flooring repairs, and plumbing repairs.
Task 2 explored potential data sources for a future national evaluation of the WRF and identified research questions that these data could help address. Key data sources included the mandatory WRF plans submitted annually to the DOE, policy and procedure manuals for grantees, and subgrantee lists of completed measures with associated costs.
Task 3 focused on WRF implementation data from 15 grantees nationwide. By comparing these plans, we identified similarities and differences in how the WRF was implemented and how implementation changed from the first to the second program year.
Task 4 synthesized the findings from the previous deliverables and includes a multi-year national evaluation plan for the WRF, aiming to answer the research questions identified during our initial evaluation. The most significant findings were the variability in program implementation and subgrantee spending across the states examined
Support for Mission Innovation and Quadrennial Energy Review
Mission Innovation
 Mission Innovation was launched in 2015 as countries around the world came together to discuss the Paris Climate Accord to accelerate the invention of tomorrow’s clean energy technologies. Mission Innovation is a global initiative of 22 nations and the European Union representing about 60% of the world’s population, 70% of GDP, and more than 80% of government investment in clean energy research. Mission Innovation’s goal is to significantly accelerate the pace of innovation, reduce costs, and make clean energy technologies widely affordable worldwide. Mission Innovation members are taking action to double their public investments in clean energy R&D over five years while encouraging collaboration among partner nations, sharing information, and coordinating with businesses and investors. Mission Innovation has established itself as a global rallying point for advancing clean energy research and innovation.
Mission Innovation was launched in 2015 as countries around the world came together to discuss the Paris Climate Accord to accelerate the invention of tomorrow’s clean energy technologies. Mission Innovation is a global initiative of 22 nations and the European Union representing about 60% of the world’s population, 70% of GDP, and more than 80% of government investment in clean energy research. Mission Innovation’s goal is to significantly accelerate the pace of innovation, reduce costs, and make clean energy technologies widely affordable worldwide. Mission Innovation members are taking action to double their public investments in clean energy R&D over five years while encouraging collaboration among partner nations, sharing information, and coordinating with businesses and investors. Mission Innovation has established itself as a global rallying point for advancing clean energy research and innovation.
In June 2016, all Mission Innovation members declared a collective baseline of $15 billion per year in clean energy R&D investment. The members have each pledged to seek a doubling in their governmental and/or state-directed clean energy research and development investment over five years, reaching around a combined $30 billion per year by 2020-2021.
In 2017, Georgia Tech worked with the Mission Innovation Secretariat, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, and Energetics, Inc., to develop best practice features of Innovation Challenges workshops. The team provided examples of the types of input gathered through collaborative expert workshops on related topics. We drew resources from past experience including workshops previously sponsored by the DOE’s Office of Basic Energy Sciences, to illustrate how well-designed workshops can provide critical information needed to address barriers and ultimately give rise to game-changing energy solutions in support of national energy strategies.
An overview of lessons learned from past workshops can be found in the following ORNL report:
Antes, Matthew, Anna Mosby, Melissa Lapsa, Charlotte Franchuk, Marilyn Brown. 2017. Workshops on R&D Opportunities in Clean Energy Innovation, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, ORNL/SPR-2017/407, http://mission-innovation.net/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/MI-Workshop-Guide-2017-October-Final.pdf (image above)
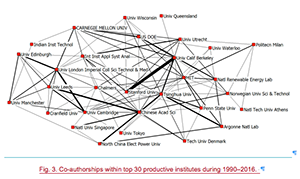
The report shows how bibliometrics can be used to support the effective design and implementation of workshops, such as relationship mapping, as shown to the right.
Quadrennial Energy Review
Georgia Tech worked with ORNL to produce two “baseline reports” for the DOE Quadrennial Energy Review 1.2, which were published in 2017.
Brown, Marilyn A., Daniel D’Arcy, Melissa Lapsa, Isha Sharma, Yufei Li. Solid Waste from the Operation and Decommissioning of Power Plants, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, ORNL/SPR-2016/774 (2017), http://info.ornl.gov/sites/publications/files/Pub60563.pdf
Emanuele Massetti, Marilyn Brown, Melissa Lapsa, Isha Sharma, James Bradbury, Colin Cunliff, Yufei Li. Environmental Quality and the U.S. Power Sector: Air Quality, Water Quality, Land Use and Environmental Justice, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, ORNL/SPR-2016/772 (2017), http://info.ornl.gov/sites/publications/files/Pub60561.pdf
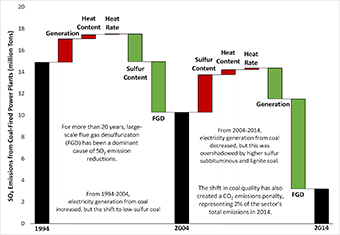
In addition, the Electricity Journal published the results of the team’s decomposition analysis of SO2 emissions from coal power plants, which identified a carbon dioxide penalty resulting from the change in types of coal burned over the past decade:
Brown, Marilyn A., Yufei Li, Emanuele Massetti, and Melissa Lapsa. 2017. “U.S. Sulfur Dioxide Emission Reductions: Shifting Factors and a Carbon Dioxide Penalty,” The Electricity Journal, 30: 17-34. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1040619016302548
